Jul 07 2022
Expectations are rising for green hydrogen production through water electrolysis1 using electricity derived from sunlight to move toward realizing a sustainable carbon-neutral society. It is essential to develop a highly-efficient water electrolysis cell2 that operates at low overvoltage3 and combine it with a solar cell appropriate for its maximum output to achieve high solar-to-hydrogen efficiency (STH)4. The research group of TSUBONOUCHI Yuta (Specially Appointed Assistant Professor), ZAKI NABEIH AHMED Zahran (Specially Appointed Associate Professor) and Professor YAGI Masayuki of the Department of Materials Science and Technology, Faculty of Engineering, Niigata University collaborated with the research group of Dr. SAYAMA Kazuhiro, Dr. SUGAYA Takeyoshi, Dr. MISEKI Yugo and Dr. MAKITA Kikuo of the Global Zero Emission Research Center (GZR) in the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) have developed a green hydrogen production system through solar water splitting using a highly-efficient water electrolysis cell and a solar cell, demonstrating that hydrogen can be produced stably for one month with the world's highest level of STH (13.9%).
Journal: ACS Applied Energy Materials
Title: Perfect Matching Factor between a Customized Double-Junction GaAs Photovoltaic Device and an Electrolyzer for Efficient Solar Water Splitting
Authors: Zaki N. Zahran, Yugo Miseki, Eman A. Mohamed, Yuta Tsubonouchi, Kikuo Makita, Takeyoshi Sugaya, Kazuhiro Sayama, Masayuki Yagi
DOI: 10.1021/acsaem.2c00768
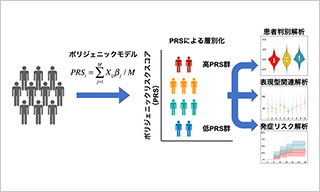
Polygenic effects on the risk of Alzheimer's disease in the Japanese population
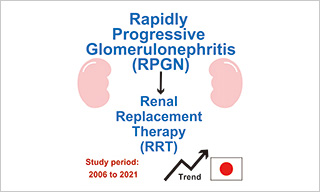
Trends in the incidence of renal replacement therapy due to rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis in Japan, 2006–2021
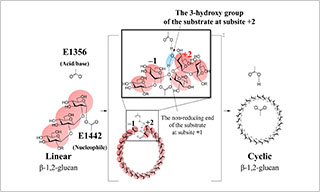
Uncovering The Cyclization Mechanism of Cyclic β-1,2-Glucan Synthase