Elucidation of plant mechanisms of response to volatile compounds from microorganisms: Paving the way for the development of environmentally friendly new plant growth promoters
Jul 24 2019
Volatile compounds (VCs) released by different phytopathogenic fungi act as signals that promote the growth of plants, photosynthesis, early flowering, and starch over-accumulation in leaves. The International research team of scientists, among others, from Niigata University Kariwa Village Advanced Agro-Biotechnology Research Center (including Specially Appointed Assistant Professor Marouane Baslam, Professor Toshiaki Mitsui) and the CSIC-Institute of Agrobiotechnology (Pamplona, Spain) (including Professor Javier Pozueta-Romero) found an important target involved in the mechanisms of VCs-promoting plant growth.
Publication Details
Title: Plant responses to fungal volatiles involve global post-translational thiol redox proteome changes that affect photosynthesis
Journal: Plant, Cell & Environment
Authors: Kinia Ameztoy, Marouane Baslam, Ángela María Sánchez-López, Francisco José Muñoz, Abdellatif Bahaji, Goizeder Almagro, Pablo García-Gómez, Edurne Baroja-Fernández, Nuria De Diego, Jan F Humplík, Lydia Ugena, Lukas Spichal, Karel Doležal, Kentaro Kaneko, Toshiaki Mitsui, Francisco Javier Cejudo, Javier Pozueta-Romero
DOI: 10.1111/pce.13601
More News
-
 Feb 13 2026 Research results
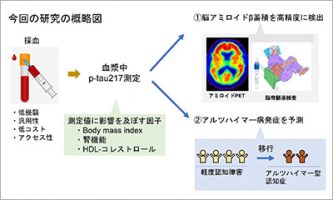
Feb 13 2026 Research resultsEvaluation of plasma p-tau217 biomarkers in detecting amyloid pathology and predicting cognitive outcomes: Observations from Japanese Alzheimer's disease neuroimaging initiative cohort
-
 Feb 12 2026 Research results
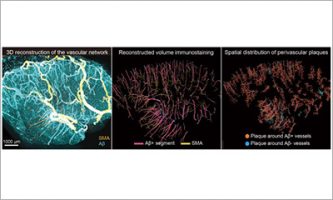
Feb 12 2026 Research resultsFrom surface to depth: 3D imaging traces vascular amyloid spread in the human brain
-
 Jan 28 2026 Research results
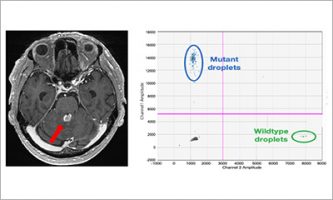
Jan 28 2026 Research resultsTreatment initiation is possible with a positive liquid biopsy in primary central nervous lymphoma patients with difficult-to-access lesions
