Sep 04 2023
A research group led by Associate Professor KANEKO Yoshikatsu and Professor NARITA Ichiei (Division of Clinical Nephrology and Rheumatology, Kidney Research Center, Niigata University Graduate School of Medical and Dental Sciences) and Associate Professor SATO Hiroe (Niigata University Health Administration Center) have found that antibody titer(Note 1) of anti-ribosomal P protein antibody that binds ribosomal P protein(Note 2), which is an autoantibody seen in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)(Note 3) patients, correlates with test results that indicate the severity of SLE, physical symptoms and blood concentrations of inflammatory cytokines(Note 4). They also reported that the higher the anti-P antibody titer, the higher the dose of corticosteroid required for treatment and that measuring the antibody titer is useful to assess the severity of SLE disease activity and select therapeutic agents. Since only a small number of cases were used for this study, investigating a larger population is necessary in the future to determine which immune cells the anti-P antibody targets to elicit an immune response and more information.
(Note 1) Antibody titer
The amount of antibodies in the blood that can be measured with a blood test.
(Note 2) Ribosomal P protein
A protein that composes ribosomes that synthesize proteins within cells.
(Note 3) Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
A disease in which the immune system reacts against the individual's own body and damages organs due to abnormalities in the immune system.
(Note 4) Inflammatory cytokine
A trace bioactive protein that is mainly secreted by immune system cells and causes inflammatory reactions.
Journal: Rheumatology
Title: Pathogenetic associations of anti-ribosomal P protein antibody titres and its subclasses in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
Authors: Yoshikatsu Kaneko*, Hiroe Sato, Ayako Wakamatsu, Daisuke Kobayashi, Kaho Sato, Yoichi Kurosawa, Eriko Hasegawa, Takeshi Nakatsue, Takeshi Kuroda, Ichiei Narita
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead402
*:corresponding author
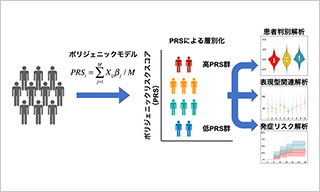
Polygenic effects on the risk of Alzheimer's disease in the Japanese population
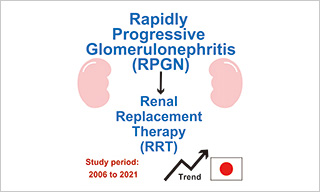
Trends in the incidence of renal replacement therapy due to rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis in Japan, 2006–2021
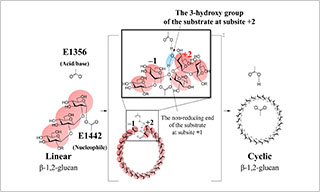
Uncovering The Cyclization Mechanism of Cyclic β-1,2-Glucan Synthase