Oct 31 2023
Various factors including obesity, diabetes, etc. are related to the etiology of steatotic liver disease (SLD) including metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) etiology and resulted in the complications in various organs. As the number of patients with SLD is increasing worldwide, it is essential to elucidate the pathological conditions and develop effective treatment methods.
The research group led by Professor KAMIMURA Kenya (Department of General Medicine, Niigata University School of Medicine/Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Graduate School of Medical and Dental Sciences, Niigata University), NAGAYAMA Itsuo (graduate student) and Professor TERAI Shuji in the same division have clarified that the dynamics of brain peptides1 are involved in the pathology of MASLD.
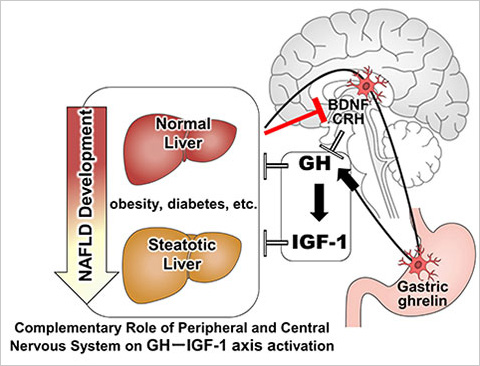
1.Brain peptide
A physiologically active peptide that exists in the brain. It mediates neurotransmissions and mental activities. A peptide is a compound consisting of two or more amino acids bonded together.
2.Autonomic neural pathway
A peripheral neural pathway that consists of two nervous systems: the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system. The autonomic neural pathway consists of two pathways: the efferent pathway, which regulates the functions of internal organs, and the afferent pathway, which conveys information from the internal organs to the central nervous system.
3.Ghrelin
A hormone produced in the stomach. Related to appetite.
Journal: Hepatology International
Title: Complementary role of peripheral and central autonomic nervous system on insulin-like growth factor-1 activation to prevent fatty liver disease
Authors: Nagayama I, Kamimura K, Owaki T, Ko M, Nagoya T, Tanaka Y, Ohkoshi M, Setsu T, Sakamaki A, Yokoo T, Kamimura H, Terai S
DOI: 10.1007/s12072-023-10601-1
The article was released in EurekAlert, the online publication of the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Polygenic effects on the risk of Alzheimer's disease in the Japanese population
Trends in the incidence of renal replacement therapy due to rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis in Japan, 2006–2021
Uncovering The Cyclization Mechanism of Cyclic β-1,2-Glucan Synthase