Identification of a protein that inhibits ubiquitination and aggregation of α-synuclein, a causative factor of Parkinson's disease
Sep 10 2019
Parkinson's disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra and striatum of brains. α-synuclein is the causative protein of Parkinson's disease. Ubiquitinated α-synuclein aggregates in nerve cells play a central role in the development of disease. A research team at Niigata University has discovered that G3BP1 protein inhibits ubiquitination and aggregation of α-synuclein. This study suggested that the G3BP1 plays a protective role in the development of Parkinson's disease by reducing α-synuclein ubiquitination and aggregation. Therefore, G3BP1 is a promising drug target for the treatment of Parkinson's disease.
Publication Details
Title: G3BP1 inhibits ubiquitinated protein aggregations induced by p62 and USP10
Journal: Scientific Reports
Authors: Sergei Anisimov, Masahiko Takahashi, Taichi Kakihana,Yoshinori Katsuragi, Hiroki Kitaura, Lu Zhang, Akiyoshi Kakita, Masahiro Fujii
More News
-
 Jun 26 2025 Research results
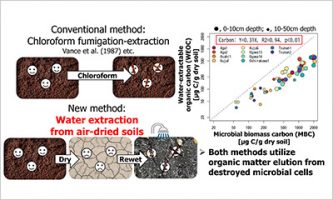
Jun 26 2025 Research resultsEstimating Microbial Biomass from Air-Dried Soils: A Safer, Scalable Approach ーRevolutionary Technique Estimates Soil Microbial Biomass Using Water-Extractable Organic Matterー
-
 Jun 03 2025 Research results
Jun 03 2025 Research resultsAssociation of rare APOE missense variants with Alzheimer's disease in the Japanese population
-
 Mar 31 2025 Research results
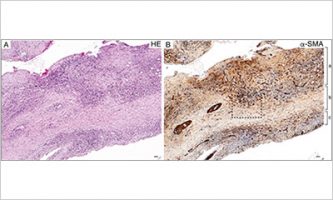
Mar 31 2025 Research resultsDiscovery of a New Pathology for Spinal Hypertrophic Pachymeningitis Caused by Vasculitides, Designated an Intractable Disease by the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare, Japan: A Path to Therapy
