Notable Research in Articles
In many academic fields, research results are first published in academic journals. Here, among the articles included in the Web of Science bibliographic database of Clarivate Analytics, we will show the number of such articles published by researchers at Niigata University and those that are particularly referred to worldwide in each field.
1. Total number of articles at Niigata University
The total number of articles and reviews by researchers at Niigata University that have been published in the last five years are shown for each year.
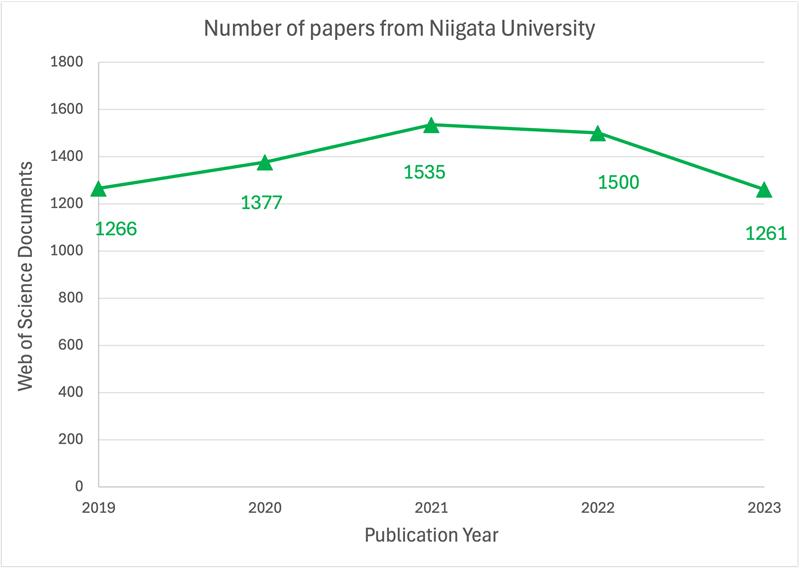 |
Filter Summary: |
2. Highly cited articles (Top 1% )
Multiple ways are available to evaluate whether an academic publication is rated high worldwide. One is to determine based on citations. Excellent publications will be cited in the publications that follow, resulting in a high number of citations. In this method, we set the group by year and field, ranking each publication based on the number of citations in descending order, measuring where in the top percentage of the group the publication is placed. Here, we will show introduce articles whose primary authors are researchers at Niigata University. The publications are from in the last five years and from those highly evaluated the most often referred to worldwide (top 1% by citations), and are cited in the top one percent for each of the 22 research fields (ESI fields) established by the Web of Science.
DENTISTRY, ORAL SURGERY & MEDICINE
Takahiro Tsuzuno, D.D.S., Ph.D.(Specially Appointed Assistant Professor), Naoki Takahashi, D.D.S., Ph.D.(Associate Professor)
Graduate School of Medical and Dental Sciences Oral Life Science Oral Biological Science, University Medical and Dental Hospital Advanced Clinical Research Center
Web site of Lab
JOURNAL OF PERIODONTAL RESEARCH
Year2021 Vol.56 Issue2 Pages 275-288
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jre.12816
Periodontitis has negative effects on several systemic diseases. In this study, we examined the effects of periodontopathogenic bacteria on intestinal diseases. We demonstrated that P. gingivalis, a major bacterium causing periodontitis, aggravates intestinal inflammation in vivo. As a mechanism, we proposed that a specific protease produced by P. gingivalis exacerbates inflammation by disrupting the intestinal epithelial barrier function
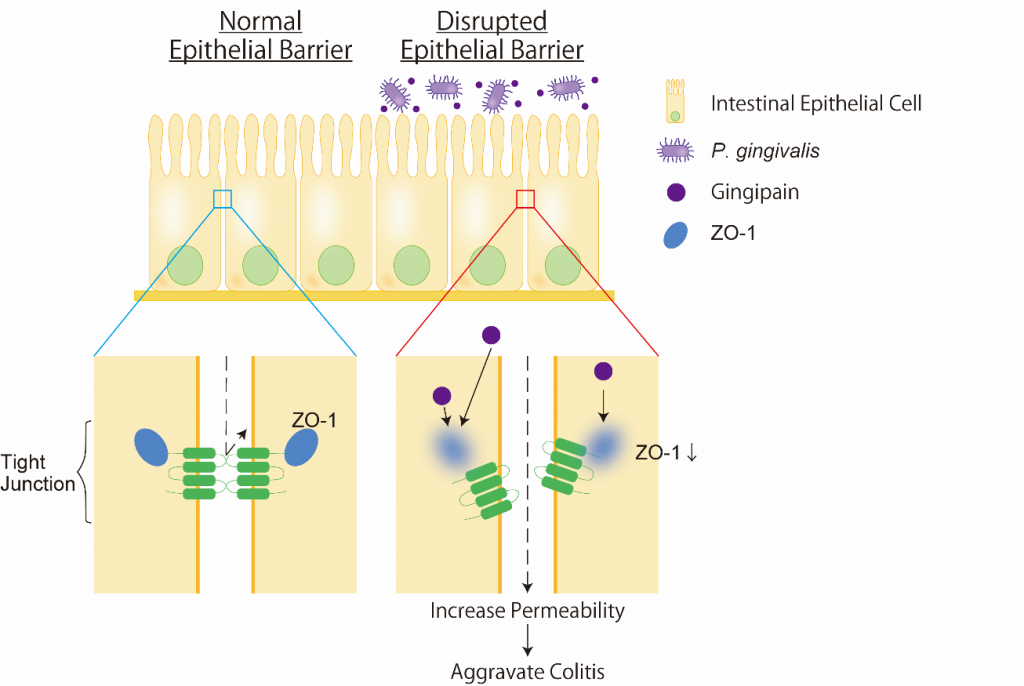
Corresponding authors : Naoki Takahashi [2], Kazuhisa Yamazaki [1]
Affiliations of corresponding authors :[1] Niigata Univ, Fac Dent, Dept Oral Biol Sci, Div Periodontol, [2] Niigata Univ, Grad Sch Med & Dent Sci, Div Oral Sci Hlth Promot, Res Unit Oral Syst Connect
Authors :Takahiro Tsuzuno, Naoki Takahashi, Miki Yamada-Hara, Mai Yokoji-Takeuchi, Benso Sulijaya, Yukari Aoki-Nonaka, Aoi Matsugishi, Kyoko Katakura, Koichi Tabeta, Kazuhisa Yamazaki
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY - OTHER TOPICS
Manako Yamaguchi, M.D., Ph.D. (Specially Appointed Assistant Professor), Kosuke Yoshihara, M.D., Ph.D. (Professor)
Graduate School of Medical and Dental Sciences Molecular and Cellular Medicine Molecular, Obstetrics and Gynecology
Web site of Lab
Three-dimensional understanding of the morphological complexity of the human uterine endometrium
iScience
Year2021 Vol.24 Issue4 Pages 102258
DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102258
While the human endometrium is essential for implantation of a fertilized egg, it is also the origin of the endometriosis and endometrial cancer. In this study, we succeed to visualize the real three-dimensional (3D) structure of the human endometrium using tissue-clearing and 3D imaging technology. Although each individual gland was thought to be independent for many years, we discovered that the endometrial glands form a network structure (Rhizome) in the stratum basalis of the human endometrium. Understanding the true 3D structure of the human endometrial glands will lead to the elucidation of the mechanisms of menstruation and implantation, and the pathogenesis of endometriosis and endometrial cancer.
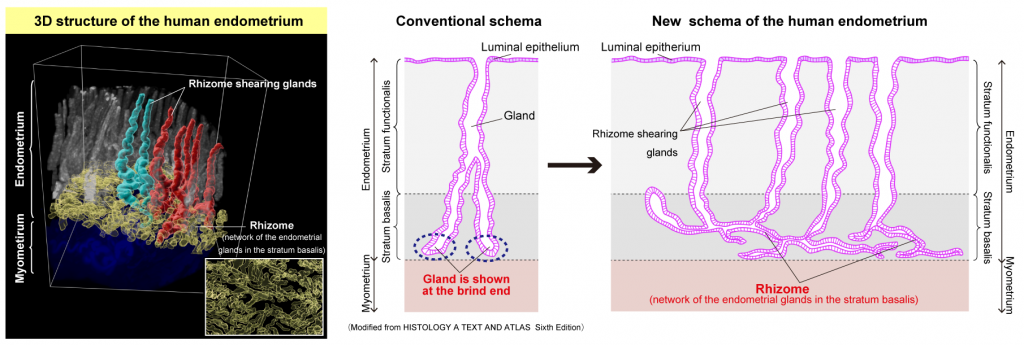
Corresponding authors : Kosuke Yoshihara [1],Kazuki Tainaka [2][3]
Affiliations of corresponding authors: [1] Niigata Univ, Dept Obstet & Gynecol, Grad Sch Med & Dent Sci, [2] Niigata Univ, Brain Res Inst, Dept Syst Pathol Neurol Disorders, [3] RIKEN Ctr Biosyst Dynam Res, Lab Synthet Biol, Suita
Authors :Manako Yamaguchi, Kosuke Yoshihara, Kazuaki Suda, Hirofumi Nakaoka, Nozomi Yachida, Haruka Ueda, Kentaro Sugino, Yutaro Mori, Kaoru Yamawaki, Ryo Tamura, Tatsuya Ishiguro, Teiichi Motoyama, Yu Watanabe, Shujiro Okuda, Kazuki Tainaka, Takayuki Enomoto
3. Characteristic research fields based on article data
Citation trends vary depending on the type of paper, publication date, and research field. The Category Normalized Citation Impact (CNCI) is an alternative indicator to the raw number of citations, enabling evaluation across different fields. This metric is the ratio of the number of citations a paper has received to the average number of citations in its research field. A paper is considered to be at the standard level for its research field when its CNCI is 1.
In this section, we present characteristic research fields at Niigata University where the CNCI exceeds 1, along with major articles that recorded high CNCI values in each field.
(Reference on CNCI: https://incites.zendesk.com/hc/en-gb/articles/25087312115601-Category-Normalized-Citation-Impact-CNCI
Research field classification: Essential Science Indicators in Web of Science Core Collection)
Space Science
Major article: “An Ice Age JWST inventory of dense molecular cloud ices”, McClure, M. K., et al., NATURE ASTRONOMY, Volume7 Issue4 Page431-+, DOI 10.1038/s41550-022-01875-w【CNCI:26.0】
Author(s) affiliated with Niigata Univ.:
Takashi Shimonishi, Sc.D. (Associate Professor), Faculty of Science
Physics
Major article: “Averages of b-hadron, c-hadron, and τ-lepton properties as of 2021”, Amhis, Y., et al. , PHYSICAL REVIEW D, Volume107 Issue 5, DOI 10.1103/PhysRevD.107.052008【CNCI:47.9】
Author(s) affiliated with Niigata Univ.:
Kiyoshi Hayasaka, Sc.D. (Professor), Faculty of Science
Geosciences
Major article: “Application of remote sensing data integration in detecting mineralized granitic zones: A case study of the Gabal Al-Ijlah Al-Hamra, Central Eastern Desert, Egypt”, Khashaba, SMA, et al., JOURNAL OF AFRICAN EARTH SCIENCES, Volume200, DOI 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2023.104855【CNCI:5.1】
Author(s) affiliated with Niigata Univ.:
Eiichi Takazawa, Ph.D. (Professor), Faculty of Science
Molecular Biology & Genetics
Major article: “Cerebrospinal fluid proteomics define the natural history of autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease”, Johnson, ECB, et al., NATURE MEDICINE, Volume29 Issue8 Page1979-+, DOI 10.1038/s41591-023-02476-4【CNCI:9.2】
Author(s) affiliated with Niigata Univ.:
Takeshi Ikeuchi, M.D., Ph.D (Professor), Brain Research Institute, Department of Molecular Genetics
Plant & Animal Science
Major article: “Reduced bone formation and increased bone resorption drive bone loss in Eimeria infected broilers”, Tompkins, Y. H., et al., SCIENTIFIC REPORTS, Volume13 Issue1, DOI 10.1038/s41598-023-27585-5【CNCI:8.3】
Author(s) affiliated with Niigata Univ.:
Toshie Sugiyama, Ph.D. (Professor), Academic Assembly Institute of Science and Technology
Clinical Medicine
Major article: “Fibroblast Activation Protein Activates Macrophages and Promotes Parenchymal Liver Inflammation and Fibrosis”, Yang, AT, et al., CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY, Volume15 Issue4 Page841-867, DOI 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2022.12.005【CNCI:11.2】
Author(s) affiliated with Niigata Univ.:
Hiroyuki Abe, M.D., Ph.D (Assistant Professor), Graduate School of Medical and Dental Sciences, Division of Gastroenterology and
Hepatology
Immunology
Major article: “Human early-onset dementia caused by DAP12 deficiency reveals a unique signature of dysregulated microglia”, Zhou, Y., et al., NATURE IMMUNOLOGY, Volume24 Issue3 Page545-557, DOI 10.1038/s41590-022-01403-y【CNCI:4.9】
Author(s) affiliated with Niigata Univ.:
Akiyoshi Kakita, M.D., Ph.D (Professor), Brain Research Institute, Department of Pathology
Mari Tada, M.D., Ph.D (Professor), Brain Research Institute, Department of Pathological Neuroscience
※Based on articles published in 2023, the above fields have been selected. The CNCI values are as of January 2025, and the researcher information corresponds to the time when the article were published.
